WHY WE NEED DMARC MONITORING?
The most popular method for phishing is email impersonation, which involves using a fake email address that looks like a legitimate one. This can be accomplished by anyone with basic knowledge of email addresses and websites.
Our DMARC Monitoring service will review reports to check for unauthorized senders spoofing your domain

Prevent Spoofed Emails

Protect Organization's Reputation

Boost Email Reach, Trust & Dellverability
High-Volume DMARC Reports for Enterprises
High-Volume DMARC Reports for Enterprises is a comprehensive feature set for organizations managing multiple domains, helping them track and report on the security of their domains. This can be difficult for enterprises managing hundreds or thousands of domains, especially in the verification phase when many domains are testing new settings. Great email security is important for enterprise reputation, and DMARC monitoring is fundamental to email authentication.
The world of email authentication is changing rapidly. Many smaller organizations and enterprises are moving to DMARC monitoring as an essential part of their email security strategy. We’re proud to offer a comprehensive, enterprise level solution for managing your Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance policy.
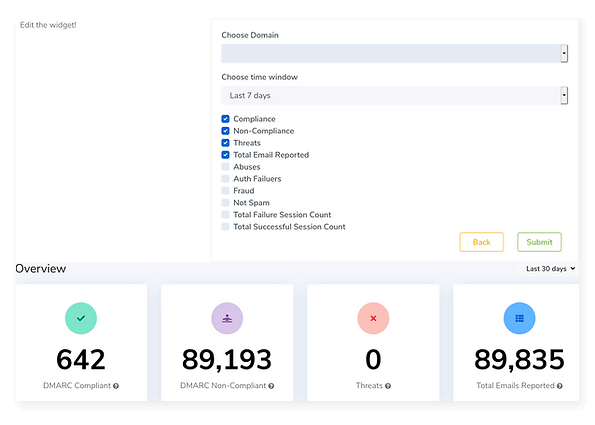
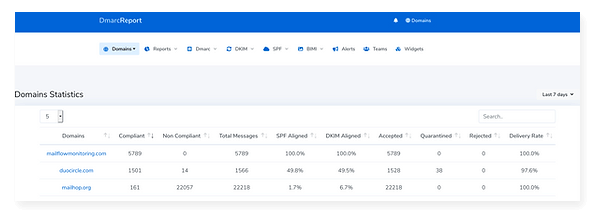
Stop Paying for Every Domain You Monitor
Most DMARC monitoring services charge a fixed rate for every domain monitored. But if you have hundreds or thousands of domains, this can add up quickly—not to mention it doesn’t work well for customers with many users across multiple companies or divisions. Not only do you have to open up a new subscription for every single customer, but you also end up paying more than what it’s actually worth.
Our unlimited DMARC reporting services at a fixed monthly rate allows you to monitor all of your domains in one place while minimizing administrative overhead.
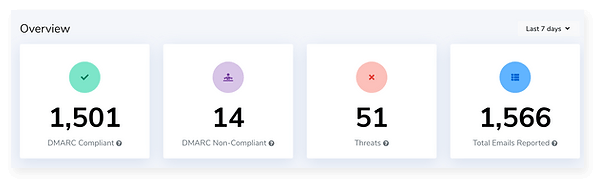
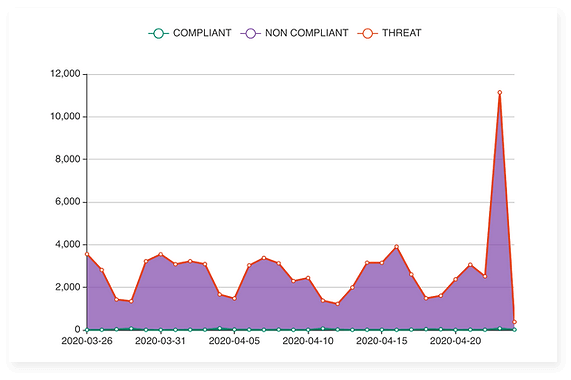
Integrate DMARC Reports into Your Apps
Our DMARC reporting solution lets users pull data directly from their reports, integrate it onto any app or dashboard, or even build their own website to access the data. You’ll collect, categorize, and analyze every email in a single place and be able to embed all of this data directly onto widget-compatible apps and dashboards.
GDPR-Compliant Email Authentication On-Demand
Our streamlined solution allows companies that are located inside the European Union or have EU customers to meet their obligations under the GDPR regulatory framework.
You can also add unlimited domains to your instance, without having to manually establish compliance policies on an individual basis.
We adhere to German data privacy regulations, and our aggregate and failure reports are covered by the GDPR regulation, which means that all reports being generated will not contain any personally identifiable information under German law.
DMARC MONITORING FEATURE

Aggregate & Forensic Reports
Aggregate & forensic reports makes your investigation easy

MTA-STS Management
Host and manage your MTA-STS policy under your domain name

TLS-RPT Reports
Implement TLS-RPT policies to enable connectivity diagnostics.

RESTful API
Aggregate & forensic reports makes your investigation easy

Widget Embedding
Display DMARC Report data directly in your apps

DNS Change Timelines
Track updates, changes, and updates your DNS records
Plans & Pricing
- Monthly
- Yearly
FREE
RM 0
/month
- 1 Domain
- 10,000 Compliant Messages
- Aggregate Reports
- Forensic Reports
- API/Widget Embeds
- 60 Day Retention
* MOST POPULAR *
STANDARD
RM 1,000
/month
- 25 Domain
- 2 Million Compliant Messages
- Everything in FREE
- Whitelabel Domain
- Groups and Teams
- MTA-STS Hosting
- TLS-RPT Reports
- 90 Day Retention
- 1 per additional Domain
ENTERPRISE
RM 4,000
/month
- 100 Domain
- 5 Million Compliant Messages
- Everything in STANDARD
- Multiple user accounts
- Bulk Domain Import
- Whitelabel Domain
- Enterprise SSO
- Enterprise SLA
- 90 Day Retention
FREE
RM 0
/month
- 1 Domain
- 10,000 Compliant Messages
- Aggregate Reports
- Forensic Reports
- API/Widget Embeds
- 60 Day Retention
* MOST POPULAR *
STANDARD
RM 833
/month
- 25 Domain
- 2 Million Compliant Messages
- Everything in FREE
- Whitelabel Domain
- Groups and Teams
- MTA-STS Hosting
- TLS-RPT Reports
- 90 Day Retention
- 1 per additional Domain
ENTERPRISE
RM 3,333
/month
- 100 Domain
- 5 Million Compliant Messages
- Everything in STANDARD
- Multiple user accounts
- Bulk Domain Import
- Whitelabel Domain
- Enterprise SSO
- Enterprise SLA
- 90 Day Retention
Frequently Asked Questions
DMARC reports help in systematic and efficient email authentication. They enable domain owners to perform the following functions:
Publish email authentication practices
State the course of action for the emails failing authentication checks
Report the action on such emails
As per the DMARC validation process, the inbound mail servers generate two types of online DMARC reports. They are:
Aggregate Reports
They are XML documents that show statistical data of incoming messages to the server that claim to be from a specific domain. They are designed to be easy for machines to read.
Forensic Reports
They are individual copies of emails that fail authentication. They are enclosed as a complete email message in a unique DMARC report format called AFRF (Authentication Failure Reporting Format). Forensic reports help in troubleshooting domain authentication and identifying malicious websites.
The aggregate DMARC report is a summarized report providing a lot of useful information. It comes in a specific format and includes the following information:
ISP information
The name of the Mailbox provider
The Mailbox provider’s email address and contact information
The report ID number
The range of the beginning and end dates
A detailed description of the DMARC record
The Header domain / From domain
The alignment settings of DKIM and SPF
The domain policy
The subdomain policy
The percentage of messages that need a DMARC policy
Summary of authentication results
The IP identified as the source of either fraudulent of legitimate email
The count of IP addresses
The disposition of the message
The DKIM authentication result
The SPF authentication result
DMARC reporting for users of Office 365 is an easy and mostly automatic process. Here is how it reports inbound and outbound emails.
DMARC for Inbound Mail
In Office 365, the program automatically detects and marks the inbound emails’ malicious domains. It subsequently sends a detailed report to the user.
DMARC for Outbound Mail
Users that work on Office 365 with the original domain, i.e., onmicrosoft.com, do not need to configure DMARC for their organization. Office 365 generates the DKIM signature for the outgoing email automatically, as SPF is already set up in the Microsoft account.
However, an organization that either uses an on-premise exchange server or a custom domain, in addition to Office 365, has to set up DMARC manually for their outbound emails.
Google usually sends DMARC reports to its users once a day. Organizations receive it at the email address specified in the DMARC record. If they turn on reports with DMARC record tags, each receiving email server from the domain will send a separate report.
Google DMARC report is sent in XML format, which includes its metadata. It essentially informs if the message from the organization’s domain passed DMARC. Other details in the DMARC report include:
The total number of outbound messages from a single IP address
The DMARC, SPF, and DKIM authentication results for outbound and inbound messages
Action that the receiving server takes, such as accepting unauthenticated messages that passed ARC authentication